Corneal densitometry changes after femtosecond laser-assisted intracorneal ring segments implantation in keratoconus
Medical hypothesis discovery and innovation in ophthalmology,
Vol. 13 No. 1 (2024),
1 July 2024
,
Page 27-34
https://doi.org/10.51329/mehdiophthal1491
Abstract
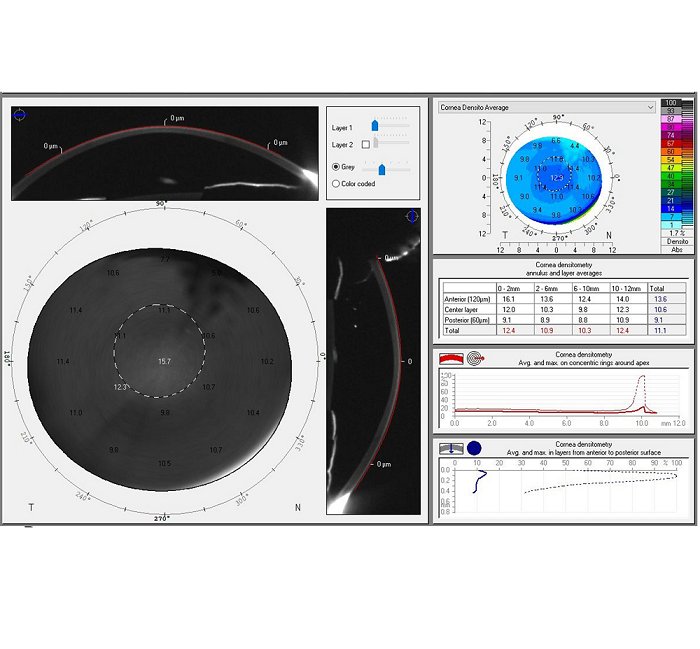
Background: Intrastromal corneal ring segments are commonly implanted in the corneas of eyes with mild-to-moderate keratoconus; however, changes in corneal densitometry (CD) after implantation are a matter of debate in the current literature. We evaluated the changes in CD 1 and 3 months after femtosecond laser-assisted Keraring implantation.Methods: This retrospective, non-comparative, multicenter, case series study included patients with keratoconus who underwent femtosecond laser-assisted implantation of double segments with 90° and 160° arc lengths or two 160° arc length Keraring segments. Demographic and baseline clinical ophthalmic data were recorded. Corneal topography and tomography data acquired using a Pentacam HR Scheimpflug tomography system (Pentacam High Resolution; Oculus, Wetzlar, Germany) with a best-fit sphere were used as a reference surface. Using the Pentacam HR, CD measurements were acquired over a corneal area of 12 mm in total and at four concentric zones (0–2, 2–6, 6–10, and 10–12 mm) of three corneal stromal depths: 120 micrometers of the anterior corneal stromal layer, 60 micrometers of the posterior corneal stromal layer, and the central layer of stroma lying between these two layers.
Results: We included 40 eyes of 40 patients, including 8 (20%) male and 32 (80%) female individuals, with a mean (standard deviation) age of 21.0 (6.4) years. We observed a significant improvement in the topographic values of steep keratometry (K), flat K, maximum K, and corneal astigmatism (all P < 0.05), but not in the mean K, thinnest corneal pachymetry, corneal thickness at the apex, back elevation, or front elevation (all P > 0.05). The mean total anterior, central, and posterior CD differed significantly among the time points, with a significant increase from the preoperative to the 1-month and 3-month postoperative visits (all P < 0.05) and no difference between those of the 1-month and 3-month postoperative visits (all P > 0.05). The mean CD for the anterior layer in the central, paracentral, and mid-peripheral zones, and the central layer in all four zones, differed significantly among time points, with a significant increase from the preoperative to the 1-month and 3-month postoperative visits (all P < 0.05), which remained unchanged from the 1-month to the 3-month postoperative visit (all P < 0.05), except for the central 2–6-mm zone, which decreased significantly from the 1-month to the 3-month postoperative visit (P < 0.001). The CD of the central 10–12-mm zone did not differ significantly in each pairwise comparison (all P > 0.05). In contrast, CD for the posterior layer in the paracentral zone decreased significantly from the preoperative to the 1-month and 3-month postoperative visits but increased, to a lesser extent, from the 1-month to the 3-month postoperative visit (all P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Femtosecond laser-assisted Keraring implantation significantly changes CD, with improvement in most topography parameters. Further longitudinal studies with larger sample sizes are required to verify these preliminary findings.
- Abstract Viewed: 0 times
- Full Text PDF Downloaded: 0 times


