Use of Rho kinase Inhibitors in Ophthalmology: A Review of the Literature
Medical hypothesis discovery and innovation in ophthalmology,
Vol. 7 No. 3 (2018),
1 September 2018
,
Page 101-111
Abstract
The use of Rho Kinase (ROCK) inhibitors as therapeutic agents in ophthalmology has been a topic of discussion for several years, particularly in the realm of glaucoma, Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy, and diabetic retinopathy. In this review, the authors provide a detailed and comprehensive overview of the published literature on the use of Rho kinase inhibitors for the aforementioned purposes. A thorough search of several databases was conducted to find sufficient literature on ROCK inhibitors. This research found strong evidence demonstrating that inhibition of Rho kinase significantly decreases IOP, increases healing of the corneal endothelium, and decreases progression of diabetic retinopathy. The main side effect of ROCK inhibitors is conjunctival hyperemia that is often present in more than half of the patients in certain formulations. Additional clinical trials investigating the reviewed treatment options of Rho kinase inhibitors are necessary to further validate previous findings on the topic. Nonetheless, it is clear that Rho kinase inhibitors have the potential to be another potent therapeutic option for several chronic diseases in ophthalmology.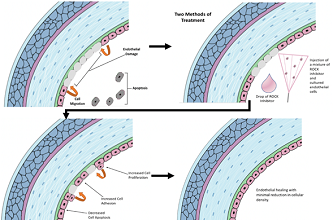
References
Hall A. Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science. 1998;279(5350):509-14. pmid: 9438836
Rao VP, Epstein DL. Rho GTPase/Rho kinase inhibition as a novel target for the treatment of glaucoma. BioDrugs. 2007;21(3):167-77. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200721030-00004 pmid: 17516712
Rao PV, Pattabiraman PP, Kopczynski C. Role of the Rho GTPase/Rho kinase signaling pathway in pathogenesis and treatment of glaucoma: Bench to bedside research. Exp Eye Res. 2017;158:23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.08.023 pmid: 27593914
Alvarado J, Murphy C, Polansky J, Juster R. Age-related changes in trabecular meshwork cellularity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981;21(5):714-27. pmid: 7298275
Johnson M. 'What controls aqueous humour outflow resistance?'. Exp Eye Res. 2006;82(4):545-57. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2005.10.011 pmid: 16386733
Bresnick GH. Diabetic maculopathy. A critical review highlighting diffuse macular edema. Ophthalmology. 1983;90(11):1301-17. pmid: 6664669
Burridge K, Wennerberg K. Rho and Rac take center stage. Cell. 2004;116(2):167-79. pmid: 14744429
Honjo M, Tanihara H, Inatani M, Kido N, Sawamura T, Yue BY, et al. Effects of rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor Y-27632 on intraocular pressure and outflow facility. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42(1):137-44. pmid: 11133858
Rao PV, Deng PF, Kumar J, Epstein DL. Modulation of aqueous humor outflow facility by the Rho kinase-specific inhibitor Y-27632. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42(5):1029-37. pmid: 11274082
Koga T, Koga T, Awai M, Tsutsui J, Yue BY, Tanihara H. Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor, Y-27632, induces alterations in adhesion, contraction and motility in cultured human trabecular meshwork cells. Exp Eye Res. 2006;82(3):362-70. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2005.07.006 pmid: 16125171
Hollanders K, Hove IV, Sergeys J, Bergen TV, Lefevere E, Kindt N, et al. AMA0428, A Potent Rock Inhibitor, Attenuates Early and Late Experimental Diabetic Retinopathy. Curr Eye Res. 2017;42(2):260-72. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2016.1183030 pmid: 27399806
Kita T. [Molecular mechanisms of preretinal membrane contraction in proliferative vitreoretinal diseases and ROCK as a therapeutic target]. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2010;114(11):927-34. pmid: 21141072
Arita R, Nakao S, Kita T, Kawahara S, Asato R, Yoshida S, et al. A key role for ROCK in TNF-alpha-mediated diabetic microvascular damage. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013;54(3):2373-83. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-10757 pmid: 23462755
Lu QY, Chen W, Lu L, Zheng Z, Xu X. Involvement of RhoA/ROCK1 signaling pathway in hyperglycemia-induced microvascular endothelial dysfunction in diabetic retinopathy. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(10):7268-77. pmid: 25400825
Rothschild PR, Salah S, Berdugo M, Gelize E, Delaunay K, Naud MC, et al. ROCK-1 mediates diabetes-induced retinal pigment epithelial and endothelial cell blebbing: Contribution to diabetic retinopathy. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):8834. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07329-y pmid: 28821742
Okumura N, Fujii K, Kagami T, Makiko N, Kitahara M, Kinoshita S, et al. Activation of the Rho/Rho Kinase Signaling Pathway Is Involved in Cell Death of Corneal Endothelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;57(15):6843-51. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-20123 pmid: 28002844
Okumura N, Nakao S, Inoue T, Pattabiraman P. Rho Kinase in Eye Disease. J Ophthalmol. 2017;2017:9281745. doi: 10.1155/2017/9281745 pmid: 28928984
Garnock-Jones KP. Ripasudil: first global approval. Drugs. 2014;74(18):2211-5. doi: 10.1007/s40265-014-0333-2 pmid: 25414122
Sturdivant JM, Royalty SM, Lin CW, Moore LA, Yingling JD, Laethem CL, et al. Discovery of the ROCK inhibitor netarsudil for the treatment of open-angle glaucoma. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016;26(10):2475-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.03.104 pmid: 27072905
Stamer WD, Braakman ST, Zhou EH, Ethier CR, Fredberg JJ, Overby DR, et al. Biomechanics of Schlemm's canal endothelium and intraocular pressure reduction. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015;44:86-98. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2014.08.002 pmid: 25223880
Okumura N, Kinoshita S, Koizumi N. Application of Rho Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Corneal Endothelial Diseases. J Ophthalmol. 2017;2017:2646904. doi: 10.1155/2017/2646904 pmid: 28751979
Kameda T, Inoue T, Inatani M, Fujimoto T, Honjo M, Kasaoka N, et al. The effect of Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor on monkey Schlemm's canal endothelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(6):3092-103. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-8018 pmid: 22491412
Isobe T, Mizuno K, Kaneko Y, Ohta M, Koide T, Tanabe S. Effects of K-115, a rho-kinase inhibitor, on aqueous humor dynamics in rabbits. Curr Eye Res. 2014;39(8):813-22. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2013.874 444 pmid: 24502505
Nakagawa H, Koizumi N, Okumura N, Suganami H, Kinoshita S. Morphological Changes of Human Corneal Endothelial Cells after Rho-Associated Kinase Inhibitor Eye Drop (Ripasudil) Administration: A Prospective Open-Label Clinical Study. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0136802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.013 6802 pmid: 26367375
Okumura N, Okazaki Y, Inoue R, Kakutani K, Nakano S, Kinoshita S, et al. Effect of the Rho-Associated Kinase Inhibitor Eye Drop (Ripasudil) on Corneal Endothelial Wound Healing. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;57(3):1284-92. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-18586 pmid: 26998714
Fusi-Rubiano W, Mukherjee C, Lane M, Tsaloumas MD, Glover N, Kidess A, et al. Treating Diabetic Macular Oedema (DMO): real world UK clinical outcomes for the 0.19mg Fluocinolone Acetonide intravitreal implant (Iluvien) at 2 years. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018;18(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12886-018-0726-1 pmid: 29486754
Arita R, Hata Y, Ishibashi T. ROCK as a Therapeutic Target of Diabetic Retinopathy. J Ophthalmol. 2010;2010:175163. doi: 10.1155/2010/175163 pmid: 20652057
Arita R, Hata Y, Nakao S, Kita T, Miura M, Kawahara S, et al. Rho kinase inhibition by fasudil ameliorates diabetes-induced microvascular damage. Diabetes. 2009;58(1):215-26. doi: 10.2337/db08-0762 pmid: 18840783
McLeod DS, Lefer DJ, Merges C, Lutty GA. Enhanced expression of intracellular adhesion molecule-1 and P-selectin in the diabetic human retina and choroid. Am J Pathol. 1995;147(3):642-53. pmid: 7545873
Lin CW, Sherman B, Moore LA, Laethem CL, Lu DW, Pattabiraman PP, et al. Discovery and Preclinical Development of Netarsudil, a Novel Ocular Hypotensive Agent for the Treatment of Glaucoma. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2018;34(1-2):40-51. doi: 10.1089/jop.2017.0023 pmid: 28609185
PubChem OCD. Compound Summary for CID 9863672, Ripasudil USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information; 2018 [updated 2018; cited 2018]. Available from: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ compound/Ripasudil.
Tanihara H, Inoue T, Yamamoto T, Kuwayama Y, Abe H, Araie M, et al. Phase 2 randomized clinical study of a Rho kinase inhibitor, K-115, in primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013;156(4):731-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2013.05.016 pmid: 23831221
Tanihara H, Inoue T, Yamamoto T, Kuwayama Y, Abe H, Fukushima A, et al. One-year clinical evaluation of 0.4% ripasudil (K-115) in patients with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Acta Ophthalmol. 2016;94(1):e26-34. doi: 10.1111/aos.12829 pmid: 26338317
PubChem OPEN CHEMISTRY Database. Compound Summary for CID 66599893, Netarsudil USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information; 2018 [updated 2018; cited 2018]. Available from: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Netarsudil.
Hoy SM. Netarsudil Ophthalmic Solution 0.02%: First Global Approval. Drugs. 2018;78(3):389-96. doi: 10.1007/s40265-018-0877-7 pmid: 29453668
Toris CB, McLaughlin MA, Dworak DP, Fan S, Havens S, Zhan GL, et al. Effects of Rho Kinase Inhibitors on Intraocular Pressure and Aqueous Humor Dynamics in Nonhuman Primates and Rabbits. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2016;32(6):355-64. doi: 10.1089/jop.2015.0116 pmid: 27266531
Kazemi A, McLaren JW, Kopczynski CC, Heah TG, Novack GD, Sit AJ. The Effects of Netarsudil Ophthalmic Solution on Aqueous Humor Dynamics in a Randomized Study in Humans. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2018;34(5):380-6. doi: 10.1089/jop.2017.0138 pmid: 29469601
Wang RF, Williamson JE, Kopczynski C, Serle JB. Effect of 0.04% AR-13324, a ROCK, and norepinephrine transporter inhibitor, on aqueous humor dynamics in normotensive monkey eyes. J Glaucoma. 2015;24(1):51-4. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0b013e3182952213 pmid: 25535688
Reitsamer HA, Posey M, Kiel JW. Effects of a topical alpha2 adrenergic agonist on ciliary blood flow and aqueous production in rabbits. Exp Eye Res. 2006;82(3):405-15. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2005.07.015 pmid: 16198336
Kiel JW, Kopczynski CC. Effect of AR-13324 on episcleral venous pressure in Dutch belted rabbits. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2015;31(3):146-51. doi: 10.1089/jop.2014.0146 pmid: 25756366
Serle JB, Katz LJ, McLaurin E, Heah T, Ramirez-Davis N, Usner DW, et al. Two Phase 3 Clinical Trials Comparing the Safety and Efficacy of Netarsudil to Timolol in Patients With Elevated Intraocular Pressure: Rho Kinase Elevated IOP Treatment Trial 1 and 2 (ROCKET-1 and ROCKET-2). Am J Ophthalmol. 2018;186:116-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2017.11.019 pmid: 29199013
Elhalis H, Azizi B, Jurkunas UV. Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Ocul Surf. 2010;8(4):173-84. pmid: 20964980
Peh GS, Adnan K, George BL, Ang HP, Seah XY, Tan DT, et al. The effects of Rho-associated kinase inhibitor Y-27632 on primary human corneal endothelial cells propagated using a dual media approach. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9167. doi: 10.1038/srep09167 pmid: 25823914
Okumura N, Ueno M, Koizumi N, Sakamoto Y, Hirata K, Hamuro J, et al. Enhancement on primate corneal endothelial cell survival in vitro by a ROCK inhibitor. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50(8):3680-7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2634 pmid: 19387080
Okumura N, Sakamoto Y, Fujii K, Kitano J, Nakano S, Tsujimoto Y, et al. Rho kinase inhibitor enables cell-based therapy for corneal endothelial dysfunction. Sci Rep. 2016;6:26113. doi: 10.1038/srep26113 pmid: 27189516
Barouch FC, Miyamoto K, Allport JR, Fujita K, Bursell SE, Aiello LP, et al. Integrin-mediated neutrophil adhesion and retinal leukostasis in diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000;41(5):1153-8. pmid: 10752954
Monickaraj F, McGuire PG, Nitta CF, Ghosh K, Das A. Cathepsin D: an MÏ•-derived factor mediating increased endothelial cell permeability with implications for alteration of the blood-retinal barrier in diabetic retinopathy. FASEB J 2016;30(4):1670-82. doi: 10.1096/fj.15-279802
Zhang XH, Feng ZH, Wang XY. The ROCK pathway inhibitor Y-27632 mitigates hypoxia and oxidative stress-induced injury to retinal Muller cells. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(3):549-55. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.228761 pmid: 29623943
Arita R. [Mechanism of diabetes-induced microvascular damage and therapeutic potential of ROCK inhibition]. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2011;115(11):985-97. pmid: 22171504
Yuan Y, Li M, To CH, Lam TC, Wang P, Yu Y, et al. The Role of the RhoA/ROCK Signaling Pathway in Mechanical Strain-Induced Scleral Myofibroblast Differentiation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018;59(8):3619-29. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-23580 pmid: 30029249
- Abstract Viewed: 1436 times
- Full Text PDF Downloaded: 1109 times


